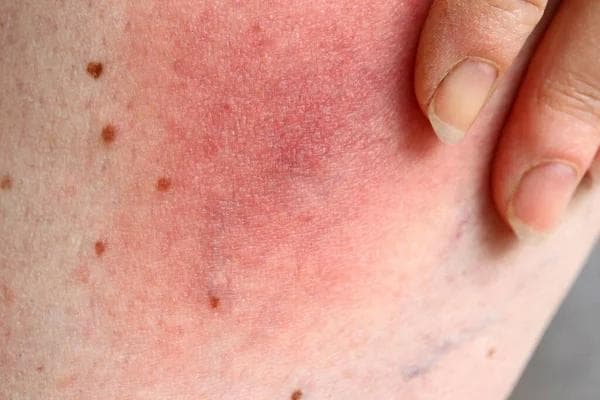
Introduction
Mottled skin, also known as livedo reticularis, is a condition that manifests as an irregular pattern of red or purple blotches on the skin. This appearance can range from mild spots to more extensive redness that affects larger areas of the body. While it is often harmless, mottled skin can be a sign of underlying health issues, making it important to understand and properly manage this condition.

What is Mottled Skin?
Mottled skin, or livedo reticularis, is characterized by a reticulated or net-like pattern on the skin, often appearing in red, purple, or bluish tones. This phenomenon occurs due to an alteration in blood circulation near the skin's surface, causing some areas to appear paler while others appear darker. Although it can appear anywhere on the body, it is most commonly seen on the limbs, such as the arms and legs.
This mottled pattern can be either temporary or permanent, depending on its underlying cause. In some cases, it may be related to temperature changes or vascular issues, while in others, it could be a symptom of a more serious medical condition.

Common Causes of Mottled Skin
Mottled skin can be caused by various conditions that affect blood circulation and the skin. Some of the most common causes include:
- Circulatory problems: One of the most common causes of mottled skin is reduced blood flow in the superficial vessels, which can occur due to extreme cold or underlying vascular diseases.
- Cold exposure: Cold can cause blood vessels to constrict, leading to the temporary appearance of mottled skin, especially in individuals with poor peripheral circulation.
- Autoimmune diseases: Some autoimmune diseases, like lupus, can cause inflammation in the blood vessels and lead to mottled skin.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as those that affect blood clotting or blood pressure, can cause mottled skin as a side effect.
- Infectious diseases: Severe infections, such as sepsis, can cause changes in blood circulation that result in mottled skin.

Is Mottled Skin Dangerous?
In most cases, mottled skin is not dangerous and may be a temporary response to factors like cold or stress. However, in some instances, it can be a sign of a more serious underlying medical condition, especially if the mottling persists or occurs alongside other concerning symptoms.
For example, if mottled skin is accompanied by pain, swelling, fever, or changes in skin color that do not go away, it could indicate circulatory problems, autoimmune diseases, or even severe infections that require immediate medical attention. It's important to assess each case individually to determine if mottled skin is simply a benign reaction or if it requires further evaluation by a healthcare professional.

Available Treatments for Mottled Skin
The treatment of mottled skin largely depends on its underlying cause. Here are some of the most common options:
| Treatment | Description |
|---|---|
| Preventive measures | Keep the skin warm and protected from the cold, wear appropriate clothing, and avoid sudden temperature changes. |
| Medical treatment | Medications to improve circulation or control inflammation, such as anticoagulants or immunosuppressants. |
| Home care | Gently massage the affected skin, apply mild heat, and keep the skin well-moisturized. |
| Alternative therapies | Options like acupuncture or herbal medicine, always under medical consultation. |
| Medical follow-up | Regularly consult with a specialist to monitor the condition and avoid serious complications. |

Impact of Climate and Temperature on Mottled Skin
Climate and temperature play a crucial role in the appearance and severity of mottled skin. Extreme cold, in particular, can cause the blood vessels near the surface of the skin to constrict, resulting in the characteristic mottled pattern. People with poor peripheral circulation are especially susceptible to these changes.
On the other hand, warm and humid climates may relieve symptoms in some individuals, while in others, they may exacerbate the condition due to excessive sweating and humidity. Understanding how your skin responds to different climate conditions can be key to managing mottled skin symptoms.

When to Consult a Dermatologist About Mottled Skin
It’s important to know when to seek a dermatologist’s opinion if you have mottled skin. While this condition is often harmless and temporary, there are situations where consulting a professional is essential:
- Persistence: If mottled skin does not go away over time or worsens, it is advisable to seek medical help to rule out more serious underlying conditions.
- Additional symptoms: The presence of other symptoms, such as pain, fever, swelling, or changes in skin color, are signs that you should consult a dermatologist.
- Medical history: Individuals with a history of vascular, autoimmune, or infectious diseases should be particularly attentive to the appearance of mottled skin and consult with a specialist if necessary.

Diet and Lifestyle to Improve Mottled Skin
Lifestyle and diet can have a significant impact on skin health, including mottled skin. Here are some key recommendations:
| Aspect | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Balanced diet | Consume foods rich in antioxidants, such as fruits and vegetables, which help improve overall skin health. |
| Hydration | Stay well-hydrated by drinking enough water throughout the day to keep the skin hydrated and healthy. |
| Regular exercise | Exercise improves blood circulation, which can help reduce the appearance of mottled skin. |
| Avoiding alcohol and tobacco | Limit alcohol consumption and avoid smoking, as these can negatively affect circulation and skin health. |
| Stress management | Practice relaxation techniques like meditation and yoga to reduce stress, which can exacerbate mottled skin. |

Conclusion
Mottled skin is a condition that can range from being a temporary and harmless phenomenon to an indicator of more serious underlying health problems. Understanding the causes, identifying symptoms, and knowing when to seek medical help are key steps in managing this condition. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, protecting your skin from the cold, and following medical advice are essential to improving skin health and preventing complications.